A
Size: a a a
2020 January 06
Ну или я плохо искал
VK
VK
Без
VK
Просто 1
VK
У меня X Compact
VK
Удобен настолько, насколько может быть удобной лопата
VK
Вот Xperia Pro збс была
VK
Маленькая и толстенькая
V
погуглил, это какая-то дотнетовская фигня
A
Если это лопата, то что же тогда остальные флагманы
VK
Araun
Если это лопата, то что же тогда остальные флагманы
Ультралопаты
V
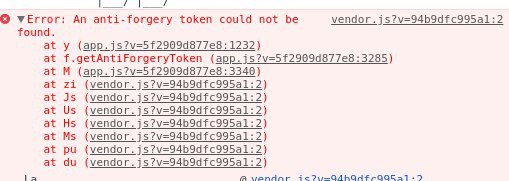
Anti-Forgery Tokens
To help prevent CSRF attacks, ASP.NET MVC uses anti-forgery tokens, also called request verification tokens.
The client requests an HTML page that contains a form.
The server includes two tokens in the response. One token is sent as a cookie. The other is placed in a hidden form field. The tokens are generated randomly so that an adversary cannot guess the values.
When the client submits the form, it must send both tokens back to the server. The client sends the cookie token as a cookie, and it sends the form token inside the form data. (A browser client automatically does this when the user submits the form.)
If a request does not include both tokens, the server disallows the request.
To help prevent CSRF attacks, ASP.NET MVC uses anti-forgery tokens, also called request verification tokens.
The client requests an HTML page that contains a form.
The server includes two tokens in the response. One token is sent as a cookie. The other is placed in a hidden form field. The tokens are generated randomly so that an adversary cannot guess the values.
When the client submits the form, it must send both tokens back to the server. The client sends the cookie token as a cookie, and it sends the form token inside the form data. (A browser client automatically does this when the user submits the form.)
If a request does not include both tokens, the server disallows the request.
V
(бесполезная хуйня какая)
С
Victor
Anti-Forgery Tokens
To help prevent CSRF attacks, ASP.NET MVC uses anti-forgery tokens, also called request verification tokens.
The client requests an HTML page that contains a form.
The server includes two tokens in the response. One token is sent as a cookie. The other is placed in a hidden form field. The tokens are generated randomly so that an adversary cannot guess the values.
When the client submits the form, it must send both tokens back to the server. The client sends the cookie token as a cookie, and it sends the form token inside the form data. (A browser client automatically does this when the user submits the form.)
If a request does not include both tokens, the server disallows the request.
To help prevent CSRF attacks, ASP.NET MVC uses anti-forgery tokens, also called request verification tokens.
The client requests an HTML page that contains a form.
The server includes two tokens in the response. One token is sent as a cookie. The other is placed in a hidden form field. The tokens are generated randomly so that an adversary cannot guess the values.
When the client submits the form, it must send both tokens back to the server. The client sends the cookie token as a cookie, and it sends the form token inside the form data. (A browser client automatically does this when the user submits the form.)
If a request does not include both tokens, the server disallows the request.
я уже хз какие куки ему нужны