S
Size: a a a
2021 July 27
S
Тут попкорн комедия
S
Первый вроде пытался на диси выехать но вб задушили и получилась хуета
S
Вышел первый трейлер «Холодного расчёта» — криминального фильма о карточном игроке, который решает отомстить жестокому полковнику, под началом которого он служил.
В фильме сыграли Оскар Айзек («Внутри Льюина Дэвиса») и Уиллем Дефо, а режиссёром стал Пол Шредер, известный как сценарист «Бешеного быка» и «Таксиста».
https://dtf.ru/cinema/810020
В фильме сыграли Оскар Айзек («Внутри Льюина Дэвиса») и Уиллем Дефо, а режиссёром стал Пол Шредер, известный как сценарист «Бешеного быка» и «Таксиста».
https://dtf.ru/cinema/810020
S
Фейк вроде
S
Вчера писали что он работает
S
Правда как я понял он щас ток продюссер
2021 July 28
S
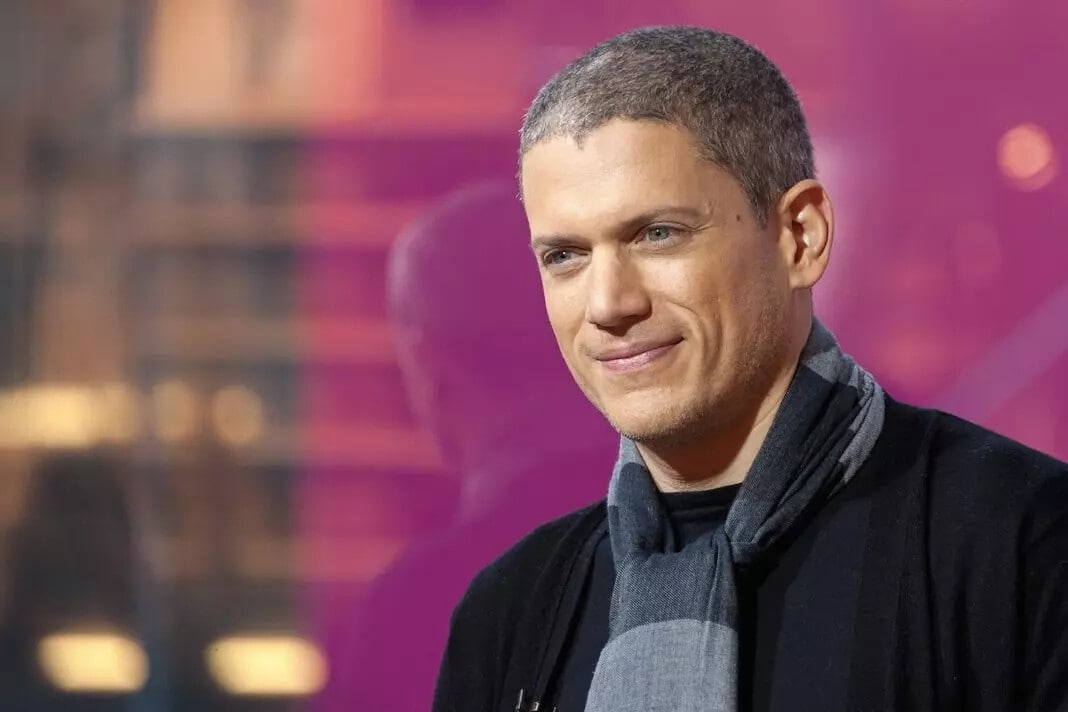

Звезда «Побега» Уэнтуорт Миллер рассказал, что год назад ему официально подтвердили аутизм. По словам его, для него диагноз был «шоком, но не сюрпризом».
Актёр отметил, что ему ещё предстоит многое узнать о расстройстве, а также под другим углом взглянуть на «пять десятилетий своей жизни».
https://dtf.ru/life/810970
Актёр отметил, что ему ещё предстоит многое узнать о расстройстве, а также под другим углом взглянуть на «пять десятилетий своей жизни».
https://dtf.ru/life/810970
VD
чот странно как-то
VD
был аутистом всю жизнь и никто не заметил?
S
Ну я хз как по аутизму, но некоторые же болезни текут вяло до момента
VD
ну это заболевание, которое проявляется с детства
VD
Autism is a highly variable, neurodevelopmental disorder[28] whose symptoms first appear during infancy or childhood, and generally follows a steady course without remission.[29] Autistic people may be severely impaired in some respects but average, or even superior, in others.[30] Overt symptoms gradually begin after the age of six months, become established by age two or three years[31] and tend to continue through adulthood, although often in more muted form.[32] It is distinguished by a characteristic triad of symptoms: impairments in social interaction, impairments in communication, and repetitive behavior. Other aspects, such as atypical eating, are also common but are not essential for diagnosis.[33] Individual symptoms of autism occur in the general population and appear not to associate highly, without a sharp line separating pathologically severe from common traits.[34]
VD
во, проявляется в младенчестве или детстве
VD
может он был сирота и всем было пох на него и не проходил обследования